BUILT ON EXPERTISE. DRIVEN BY EXCELLENCE.
INDUSTRIAL HIGH POWER BATTERY CHARGERS
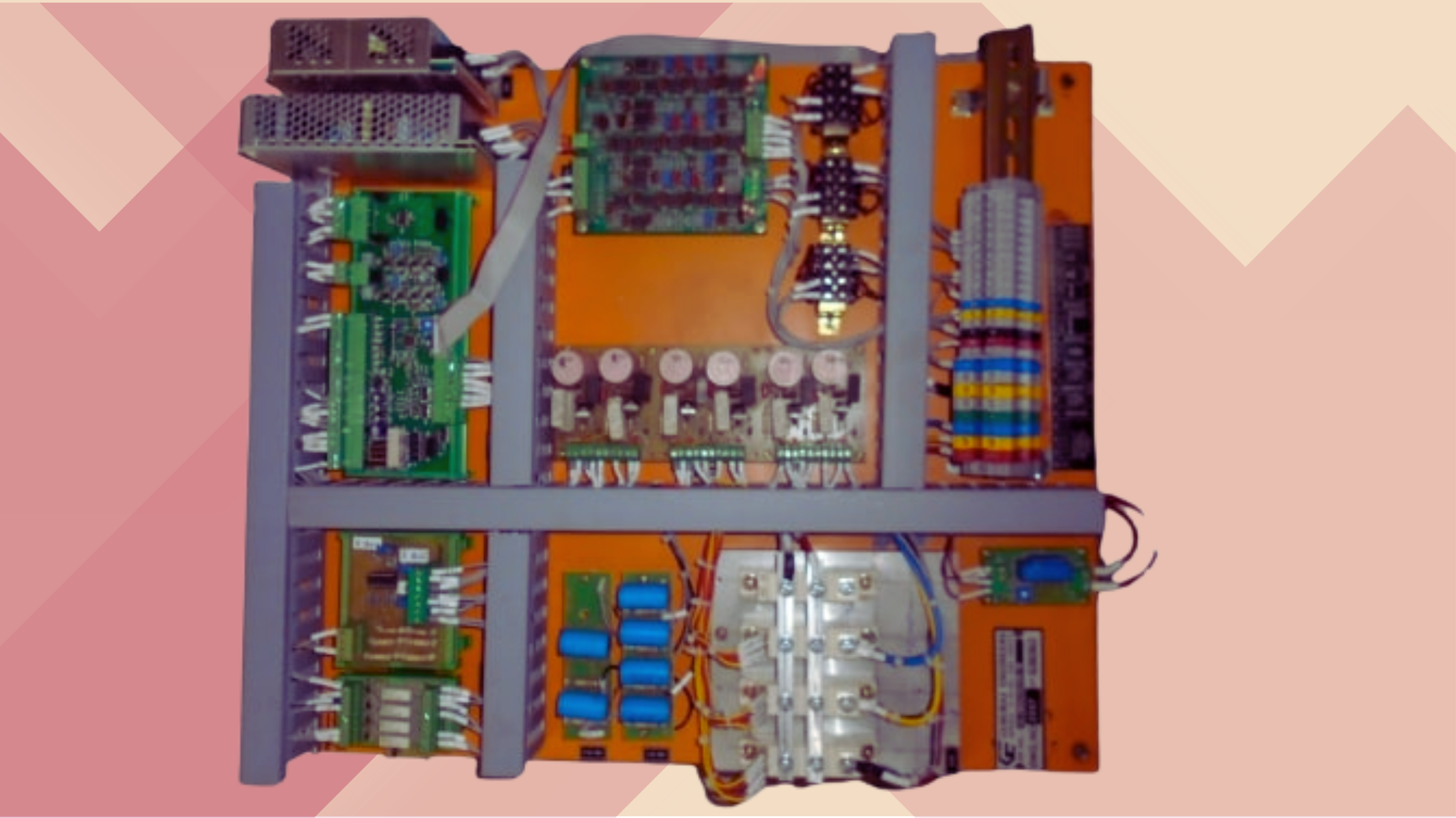
Features:
- Has a built in surge suppressor and line filter
- It has short circuit and over charge protection with overload cut off system
- The design is based on latest technology micro controller
- The charger maintains Communication protocols like RS-232/MODBUS
- Voltage ranges of 24V/48V/110V/220V with a current rating up to 200 Amps or more
Applications:
- DCS control panels
- Automotive battery charging
- Thermal projects
- Sugar industries
- Material handling equipment
INDUSTRIAL HIGH POWER BATTERY CHARGERS
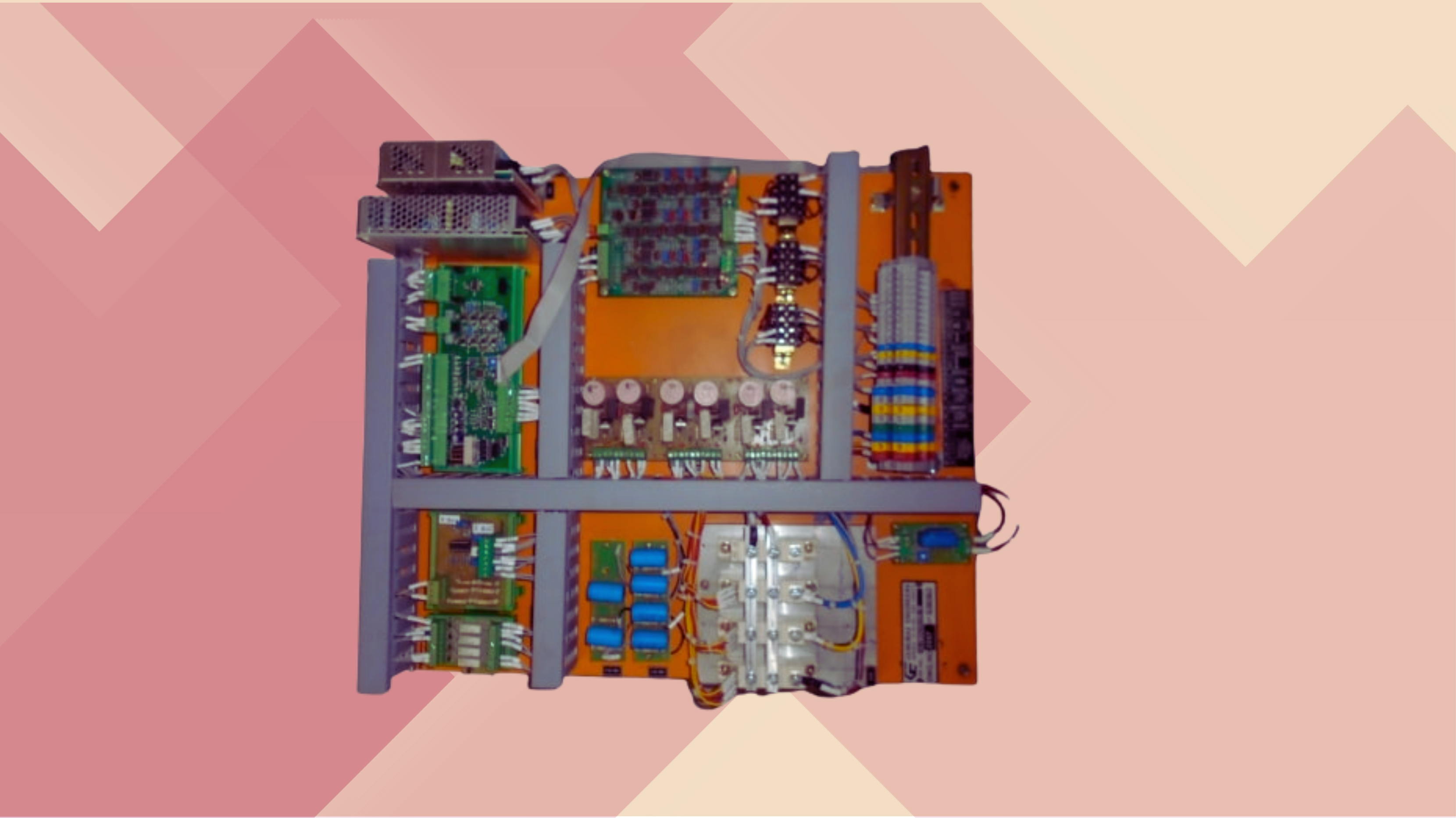
Product Details:
Features:
- Has a built in surge suppressor and line filter
- It has short circuit and over charge protection with overload cut off system
- The design is based on latest technology micro controller
- The charger maintains Communication protocols like RS-232/MODBUS
- Voltage ranges of 24V/48V/110V/220V with a current rating up to 200 Amps or more
Applications:
- DCS control panels
- Automotive battery charging
- Thermal projects
- Sugar industries
- Material handling equipment
Specifications:
Rating – Specifies the power capacity of the system, typically measured in kW or kVA, indicating the maximum load it can handle.
AC Input – Refers to the alternating current (AC) voltage and frequency supplied to the system, such as 230V or 400V at 50/60Hz.
Ripple – Represents the small fluctuations or variations in DC voltage after rectification, usually measured in millivolts (mV), affecting the performance of sensitive equipment.
Efficiency – Denotes the ratio of output power to input power, expressed as a percentage, indicating how effectively the system converts energy with minimal losses.
Rectifier – A component that converts AC to DC, typically using diodes or thyristors, ensuring stable DC output for further processing or storage.
DCDB (DC Distribution Board) – A panel used to distribute DC power to various loads, equipped with circuit breakers, fuses, and monitoring devices for protection and control.
Indications – Visual or audio signals (LEDs, alarms, or displays) that provide system status, such as power on, fault conditions, or battery status.
Metering – Measurement of electrical parameters like voltage, current, power, and energy consumption, often displayed on digital or analog meters for monitoring.
Protection – Includes safety mechanisms such as overvoltage, short circuit, surge, and thermal protection to prevent damage to the system and connected equipment.


